More information on Cochlear Implants
What is a Cochlear Implant?
A Cochlear Implant bypasses the damaged parts of the inner ear (cochlea) and delivers electrical impulses to the auditory nerve, which, in turn, sends information to the brain.
Who is a candidate for a Cochlear Implant?
A Cochlear Implant can help people who:
- have moderate to profound hearing loss in both ears
- have profound hearing loss in one ear with normal hearing in the other ear
- who receive little or no benefits from hearing aids
How does a Cochlear Implant works?
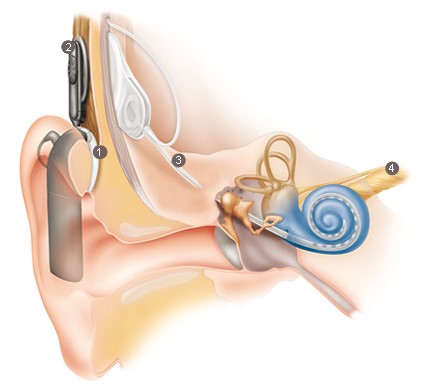
External Component
- A sound processor, worn behind the ear, captures the sound and turns it into detailed digital information.
- The sound processor transmits the digital-coded sound through the coil on the outside to the implant.
Internal Component
- The implant turns the digital-coded sound into electrical impulses, sending them along the electrode array in the cochlea.
- The hearing nerve sends the impulses to the brain, where they are interpreted as sound.